Why Google can’t count results correctly
Have you ever noticed the alleged number of search results when you use the google search? What if I tell you that the number is wrong?
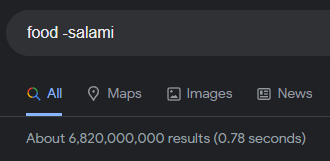
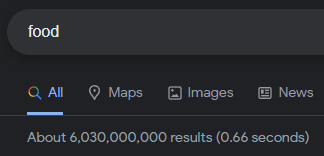
Noticed that you can do a search, then repeat the same search and “subtract” a word (in this case salami) from your original set, and Google will return more matches — not less. It shouldn’t happen, right?
Another weird behavior happens when you click until you reach the last page of the google results:
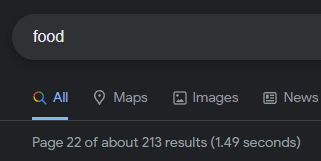
Now after reaching the last page of the search results google only shows a total number of 213 results and the note "In order to show you the most relevant results, we have omitted some entries very similar to the 213 already displayed. If you like, you can repeat the search with the omitted results included." - So let's try this.
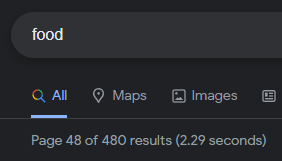
At this point you clearly noticed that even with the option "omitted results included" 480 results are much less than the 6 billion results google "showed" at the beginning on page 1.
So does google only have 480 results for food?
No, of course not! When we searched for food, Google did a fast lookup and found it had somewhere around 6 billion matching pages for that word. This can also include pages that don’t actually contain the word but have synonyms of it, along with pages that don’t have the word but are relevant because people link to them with the word food in the hyperlinks. When we searched for food -salami Google had to "think" harder about the query. It’s like when someone asks you a question that you know the answer to off the top of your head. Google gets asked about food all the time - and has stored the answer ready for usage on the memory. But when we query google for food -salami Google had to dig deeper and it discovers that it has even more pages about food (even when we filter out the word salami) out there than it thought it had originally.
Additionally, there are other factors that should be mentioned — Google has a lot of data centers around the globe with giant copies of its search index spread out across the different storage facilities. Imagine a library that has exact branches across the world. Technically, they’re “mirrors” of each other. In reality, each library might be missing a few books here and there for a variety of reasons. That can lead to different results for different users. And the Google algorithm as well influences the search results.
As well there is a official statement from Google about the problem: When you perform a search, the results are often displayed with the information: Results 1 - 10 of about XXXX. Google's calculation of the total number of search results is an estimate. We understand that a ballpark figure is valuable, and by providing an estimate rather than an exact account, we can return quality search results faster. In addition, when you click on the next page of search results, the total number of search results can change. In this case, we realize that some of the query results are duplicates, and collapse those duplicates so that you can find the specific result you're looking for more easily. Collapsing the duplicates decreases the estimated number of results, as well as the overall number of results pages.
But why does google only show a few hundred results?
The truth is, that Google does not only have a few hundred results for the search queries. To save computing power, google limits the amount of search results to a few hundred that are, according to the google algorithm, the most interesting ones. In this case, if you want more results, you have to use more keywords or another search engine. A good overview of alternatives can be found at the Semrush Blog.